Introduction
Cybersecurity threats are escalating, placing businesses at significant risk without robust protective measures such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). Passwords alone, which were once the norm, are no longer adequate to prevent sophisticated cyberattacks. This blog discusses the risks of not using MFA and offers actionable solutions to protect your digital assets more effectively.
Table of Contents
- What is Multi-Factor Authentication?
- Why Passwords Alone Are Not Enough
- Key Risks of Not Using MFA
- Solutions to Risk Mitigation
- Practical Examples and Case Studies
- Conclusion: Strengthen Your Security Today
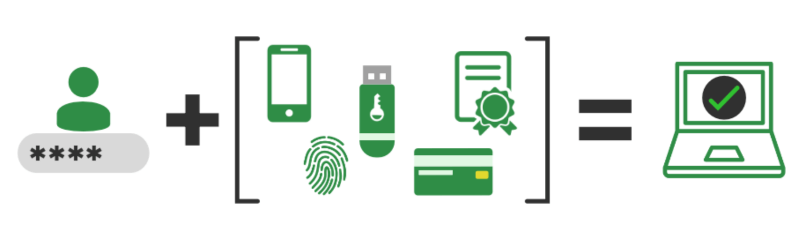
What is Multi-Factor Authentication?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security protocol that requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to an account or system. These factors typically include:
- Something you know: a password or PIN.
- Something you have: a security token, mobile device, or hardware key.
- Something you are: biometric data like fingerprints or facial recognition.
This layered approach significantly enhances security by making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access, even if one factor (like password) is compromised.
Why Passwords Alone Are Not Enough
While passwords have long been the standard for authentication, they are inherently vulnerable to various attacks, including:
- Phishing Attacks: Malicious actors trick users into revealing their credentials through deceptive emails or messages.
- Brute-Force Attacks: Automated attempts to guess passwords using various combinations.
- Credential Stuffing: Reusing stolen credentials from one branch to access other accounts.
Passwords can be vulnerable to brute-force attacks, phishing, and credential stuffing. In 2023, 81% of hacking incidents were attributed to weak or stolen passwords, according to a leading cybersecurity report.

Key Risks of Not Using MFA
- Risks of Phishing Attack Increase
- Vulnerability to Credential Theft
- Compliance Issues
- Data Breaches and Financial Loss
- Loss of Customer Trust
- MFA Fatigue
Cybercrooks can easily trick users into providing their credentials; however, MFA provides an additional layer that significantly reduces the effectiveness of phishing attacks. However, advanced techniques, such as man-in-the-middle attacks, can still exploit vulnerabilities with MFA in place.
Without MFA, stolen passwords give attackers direct access to sensitive data and accounts. By requiring multiple factor for authentication, MFA reduces the chances of unauthorized access even if login credentials are compromised.
Many industries, including finance and healthcare, require MFA to comply with regulatory standards such as GDPR and PCI DSS. Non-compliance could result in significant penalties and reputational damage.
In 2023, the average cost of a single data breach was $4.45 million. MFA can mitigate such losses by preventing unauthorized access.
Clients care about security; a failure to protect data not only damages reputation but can also lead to long-term loss of customer loyalty and trust.
As organizations adopt MFA, users may experience “MFA fatigue” leading them to approve authentication requests without verifying their legitimacy. This can create vulnerabilities if attackers bombard users with requests in an attempt to gain access through user complacency.

Solutions for Risk Mitigation
- Deploy MFA Across High-Risk Systems : Start with accounts associated with emails, online banking/financial platforms, admin panels. Not least, this would also encompass software and vulnerability scanning.
- Educate Personnel : Regular training on what a phishing attempt looks like, as well as simulating secure login practices should become a priority.
- Educate Personnel : Regular training on what a phishing attempt looks like, as well as simulating secure login practices should become a priority.
- Upgrade MFA Technology : SMS coders are vulnerable to interception, while hardware tokens generate a unique code that is much harder to intercept, providing a higher level of security.

Practical Examples and Case Studies
A major e-commerce company reduced account takeovers by 90% within six months of adopting a comprehensive MFA solution that included biometric verification and hardware tokens.
Example:
Banks using biometric verification report significantly fewer fraud incidents compared to those relying solely on PINs.
Conclusion: Strengthen Your Security Today
Failing to implement MFA exposes companies to significant risks, including financial losses, reputational damage, and costly compliance penalties. While implementing MFA is no longer an option but a must-have, the organizations need to keep monitoring threats and adapt to changes in the nature of cyber threats.
Strengthen your security today by adopting advanced MFA solutions. Protect your digital assets with secure and reliable hosting services from VPS9.



