Introduction to SSH
Whether you’re trying to administer a Linux server, set up a VPS hosting plan, or just make all the tweaks you can to speed up your website, if you’ve been working with the server, you have of course come across the term SSH. In an increasingly digital world where private access to your servers is essential, SSH (Secure Shell) is a lot more than just a tool—we consider it a foundational technology.
SSH is essentially a secure encrypted connection that gives users access to a remote system, thus allowing you to control files and directories, and execute commands. SSH lets you perform a variety of actions and changes to your server—deploying applications, making server settings, updating databases, etc, all securely and remotely.
In this blog, we’re going to explain SSH in layman’s terms; how it works, and its relevance to our current web hosting landscape.
Understanding SSH: Definition and Purpose
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a network protocol for connecting to a remote computer or server securely. This means communications are encrypted to protect things like passwords, configuration files, and the transferred content from being captured maliciously.
SSH was developed to supplant insecure protocols such as Telnet and rlogin and quickly grew popular for remote administration of servers. If you are working with a cloud server, a Linux VPS, or a dedicated hosting environment, SSH is the most secure way to work directly with your server.
Unlike cPanel, Plesk, or similar graphical user interfaces, SSH provides a very powerful command-line interface (CLI). Admittedly, the CLI does look like an intimidating mess at first unless one has been formally trained; however, it makes new users feel like they control the computer, especially when they see how fast the CLI responds as well as the ease of writing scripts that make monotonous daily tasks nearly effortless.
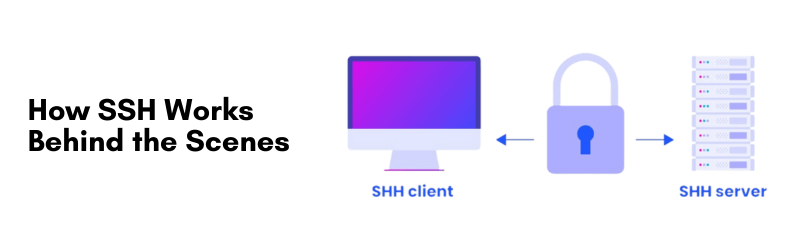
How SSH Works Behind the Scenes
Fundamentally, SSH operates as a client/server model. The user (client) makes a connection to a remote machine (server) over an unsecured network, but the protocol takes care of encryption and authentication.
The process involves:
- Initiation: A client sends a request to connect through a specific port, typically, port 22.
- Authentication: The server authenticates the client, using credentials (username/password) or cryptographic keys.
- Encryption: Once authenticated, an encrypted session is established such that every command or file transfer is encrypted.
SSH employs robust encryption standards such as RSA, AES, and Ed25519, making it extremely difficult for hackers to hijack. Most Linux hosting environments come with OpenSSH already installed, which is the most commonly used implementation of SSH.
Why SSH Matters in Web Hosting
When selecting a web hosting provider, particularly for developers or companies using resource-heavy applications, SSH access is an important consideration.
Here’s why SSH usage matters to hosting:
Full Server Control
SSH provides you full access to your server command-line interface. This is important for custom configurations, updates to the server, and troubleshooting.
Increased Security
All communication is encrypted end-to-end so there really is no way for unauthorized people to gain access but you don’t want that malicious hacker anywhere near when using a public network.
Fast Performance
A command line interface via an SSH connection always outperforms control panels or web UI interfaces. Efficiency is important when managing chores like moving files, installing software or monitoring your server’s performance.
Ideal for VPS and Dedicated Hosting
Shared Hosting types of services will usually limit access but VPS hosting and dedicated servers will typically allow all users access via an SSH connection providing an environment for users to configure a server for a specific project or type of infrastructure.
For example if you were to take advantage of a VPS service provider like ResellBox VPS Hosting that provides SSH access to all of their VPS Hosting Plans you can create a boilerplate developer environment for modern web development.

SSH vs FTP and Other Access Methods
For many users, SSH is often confused with FTP (File Transfer Protocol) or Telnet. Though they share similar capabilities, the security and functionality can be quite different.
FTP is designed entirely for file transfers. FTP does not have the encryption and command execution functionality that SSH provides. There are several secure versions of FTP, including FTPS or SFTP (while SFTP actually uses SSH), but regular FTP is insecure.
Telnet was once used for remote command execution, however, it is unauthenticated, unencrypted, and generally insecure. In fact, it is unencrypted and therefore sends your data in plain text (not good for use in a web hosting or production setting). SSH includes both file transfer and full access to the entire remote system – providing a complete solution for remote server control.
For instance, developers utilize SCP (Secure Copy Protocol) and SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) both of these utilities use the SSH protocol to securely transfer files without having to use a separate FTP utility
How to Use SSH for Server Management.
Using SSH starts with having the right credentials and tools. Here’s how to set up and connect using SSH:
Step 1: Enable SSH on Your Hosting Account
Most hosting companies will give you SSH access, but you’ll need to turn that on via a control panel like cPanel or DirectAdmin. If you’re on ResellBox, this is easily activated in a couple of clicks.
Step 2: Install an SSH Client
- If you’re on Linux or Mac OS, the Terminal app has SSH built in.
- If you’re on Windows, PuTTY, MobaXterm, and the newer Windows Terminal are nice options.
Step 3: Connect Using SSH Command
Use the following command in your terminal:
ssh username@yourserverip
You’ll be prompted to enter your password. If using key-based authentication, make sure your private key is configured properly.
Step 4: Perform Server Operations
Once logged in, you can run commands like:
- cd to change directories
- nano or vim to edit files
- top or htop to monitor server resources
- sudo for administrative tasks
SSH also allows the automation of tasks through scripting. For advanced users, it’s possible to schedule cron jobs, install LAMP stacks, or deploy entire websites from repositories—all via SSH.

Key Features and Security Advantages
SSH isn’t just about access—it’s about secure, streamlined, and professional server management. Some of the core benefits include:
Public Key Authentication
Instead of typing a password each time, you can use an SSH key pair to create a login that is both safe and fast. The private key is stored on your machine, while the public key is registered on the server.
Encrypted Tunneling
SSH can create encrypted tunnels for other services. Encrypted tunnels mean you can transport many kinds of data, like emails, databases, and HTTP traffic, safely.
Port Forwarding
Use SSH to connect to other restricted access services that are running on remote servers; This is a powerful feature you can use for debugging or when you need to access internal applications.
Logging and Session Tracking
Every SSH session can be audited because it can be logged, which is a necessity in a corporate or multi-user environment
While SSH is more than a secure login method; it is a secure framework to rely on when managing digital infrastructure.
Conclusion
With the evolution of cybersecurity protocols, remote work conditions, and digital frameworks, SSH remains one of the most consequential components of web hosting and managing servers.
Whether you manage a personal blog hosted in a Linux VPS, enterprise apps on a dedicated server, or numerous sites as a cloud hosting provider, SSH provides performance, security, and flexibility.
If you plan to use a hosting provider in 2026, I would recommend selecting a host that offers full SSH access, such as ResellBox, for secure and scalable server management for businesses or developers.
As web applications grow in complexity and are increasingly business-performance critical, SSH will remain the foundation of secure, professional, and reliable web hosting.



