Table of Contents
- Introduction to Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
- How Does Automatic Speech Recognition Work?
- Key Components of Automatic Speech Recognition Systems
- Applications of Automatic Speech Recognition Technology
- Advantages of Automatic Speech Recognition
- Challenges and Limitations of Automatic Speech Recognition
- Future of Automatic Speech Recognition Technology
- Conclusion
Introduction to Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), or speech-to-text technology, enables machines to transcribe spoken language into written text. Users can interact with computers, smartphones, and other devices via spoken commands instead of typing, thanks to ASR software. While ASR is found throughout modern day technology, it is used for a variety of purposes, especially general assistive technology, transcription, virtual assistants, and several other areas. Over time, increased access to machine learning has enhanced ASR’s use and reliability across multiple domains.
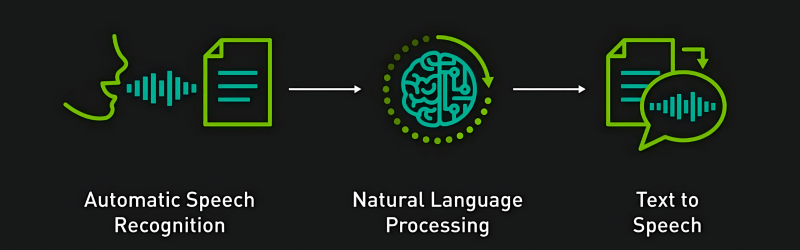
How Does Automatic Speech Recognition Work?
Automatic speech recognition systems use a number of complex processes that analyze sound waves and convert them to text. ASR begins with audio input, followed by preprocessing (noise removal), feature extraction (identifying speech patterns), pattern recognition (using ML models), and finally text conversion. Advanced automatic voice recognition algorithms utilize artificial intelligence (AI) and Natural language processing (NLP) to improve the detection of speech output. Real-time ASR processing is now available to consumers and enterprises across the world as a result of the advancements in cloud computing.
Key Components of Automatic Speech Recognition Systems
An Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system comprises several essential components:
- Acoustic model: Recognizes phonetic sounds in speech.
- Language model: Predicts word sequences based on linguistic patterns.
- Pronunciation dictionary: Ensures accurate word recognition.
- Speech processing algorithms: Leverage deep learning for improved accuracy.
- Noise reduction technology: Enhances clarity by minimizing background noise.
- Deep learning integration: AI-driven models refine Automatic Speech Recognition accuracy.
- Continuous learning and user adaptation: Allows Automatic Speech Recognition systems to improve over time, adapting to different accents and speaking styles.
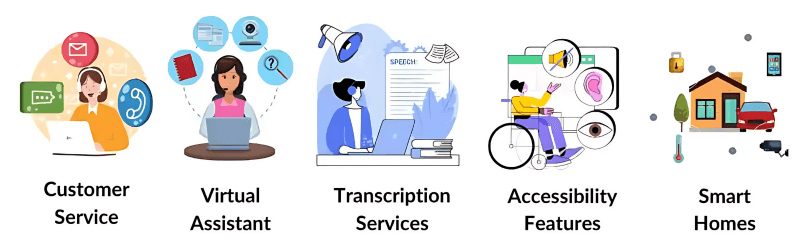
Applications of Automatic Speech Recognition Technology
ASR technology is widely used across multiple industries. Voice recognition algorithms allow Siri, Google Assistant, Alexa, and other virtual assistants to process user requests. Transcription services convert audio into text for legal documents, business meetings, and journalism. Automated voice response systems are utilized to help customer service. Healthcare providers utilize Automatic Speech Recognition when creating dictated notes, and accessibility tools assist those with disabilities. Automatic Speech Recognition is also utilized in technologies for real-time language translation, call center automation, and voice control in cars.
Voice search, a rapidly growing ASR application, lets users perform web queries by speaking. Automatic Speech Recognition is also being used in conjunction with home automation systems because smart home appliances are so prevalent, where voice command is used to control lighting, appliances, and security. ASR’s versatility is further enhanced when paired with wearable technologies like smartwatches and augmented reality glasses.
Advantages of Automatic Speech Recognition
ASR enables faster text entry, boosting efficiency. It enhances the user experience on smart technology, improves access to information by individuals with disabilities, encourages hands-free multitasking, and boosts productivity by lessening the burden of human transcription. Businesses leverage speech recognition tools to facilitate customer service automation, optimize voice searches, and streamline workflows.
By reducing typing demands, ASR allows professionals (e.g., in healthcare, legal, and education) to focus on higher-value tasks. Automatic Speech Recognition implementation in call centers has enhanced customer service efficiency and streamlined processes by eliminating wait times. Furthermore, multilingual ASR systems have begun to appear to address language barriers in international communications.
Challenges and Limitations of Automatic Speech Recognition
Automatic speech recognition has its drawbacks in addition to its advantages. Background noise, accents/dialects, and homophones (words that sound alike) can degrade accuracy. Some languages lack robust ASR models, and privacy/data ownership concerns persist. Finally, for accurate voice recognition, training AI models consistently and quality datasets is critical.
The reliability of ASR differs, for instance, according to its environment. While ASR does well with minimal noise, it struggles in noisy contexts such as busy offices, public spaces, or industrial environments. Since voice data collection is often required for Automatic Speech Recognition systems to improve performance, ethical concerns about data privacy arise. There is still a challenge to maintain user confidence around confidentiality while maintaining ASR reliability.
Future of Automatic Speech Recognition Technology
Recent developments in AI, deep learning and Natural language processing (NLP) are promising for Automatic Speech Recognition. Advanced neural networks will boost ASR accuracy, enable real-time translation, and adapt to individual speech patterns. The use of voice-enabled smart appliances will proliferate with increased IoT integration and voice authentication will be enhanced with security. Companies will continue to leverage spending on AI powered speech-enabled text technologies to increase automation and voice-enabled user interfaces during the purchase consideration and on a continuous basis.
ASR is expected to improve global connectivity by supporting effective cross-lingual communication. In customer service, AI-enabled sentiment analysis can enhance ASR by recognizing emotional tone and sentiment. Additionally, research on brain-computer interfaces (BCI) may lead to ASR systems that facilitate understanding of neural speech signals, paving the path for advancements in assistive technology and human-computer interaction.
Conclusion
Automatic Speech Recognition is revolutionizing how humans interact with machines. Its diverse applications across different industries will continue its value proposition of enhanced accessibility, improved productivity, and greater convenience. Although there are still barriers to overcome, further developments in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and speech-to-text technology will gradually improve Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) technology and overall user experience for practical everyday applications. As voice recognition software develops and evolves, it will greatly support organizations during their digital transformations.
The use of ASR is likely to increase rapidly in the near future, with new developments and innovations advancing this technology. From improving virtual assistants to facilitating seamless human-computer interaction, ASR will persist in transforming the methods we communicate with technology. Companies and researchers are working toward improving ASR models with a focus on making them more inclusive, accurate, and safe. The promise of the future of ASR is greater accessibility and increased efficiency, making human spoken communication with devices even more natural.



